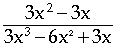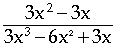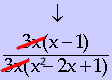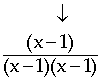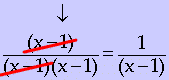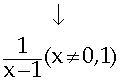Error : Please Click on "Not a robot", then try downloading again.
Simplifying rational expressions requires good factoring skills. The twist now is that you are looking for factors that are common to both the numerator and the denominator of the rational expression .
Steps to simplify rational expressions
1) Look for factors that are common to the numerator & denominator.
2) 3x is a common factor the numerator & denominator. Note that it is clear that x ≠0.
3) Cancel the common factor.
4) If possible, look for other factors that are common to the numerator and denominator. In our example, we can use foil in reverse to factor an (x − 1) in the denominator and further cancel this binomial from both the numerator and the denominator.
5) After cancelling, you are left with 1/(x-1).
6) The final simplified rational expression is valid for all values of x except 0 and 1.
How to Simplify Rational Expressions Example
Problem 1
Step 1
Factor each numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^2 + 3x}{x^2 - 4x - 21}
= \frac{x(x + 3)}{(x - 7)(x + 3)} \end{align*}
$$
With the denominator factored, we know that our final answer will have to restrict the values $$x$$ so that $$x \neq -3$$ and $$x \neq 7$$ .
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x(x + 3)}{(x - 7)(x + 3)}
& = \frac{x\cancelred{(x + 3)}}{(x - 7)\cancelred{(x + 3)}}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x}{x - 7};\quad x \neq -3
\end{align*}
$$
Note that the other restriction (that $$x \neq 7$$ ) is still explicit in the final expression.
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^2 + 3x}{x^2 - 4x - 21} = \frac{x}{x - 7};\quad x \neq -3
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 2
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^2 + 4x + 4}{x^2 - 4}
=
\frac{(x+2)(x+2)}{(x+2)(x-2)}
\end{align*}
$$
We can see that, based on the factored denominator, our answer has to restrict the $$x$$-values so that $$x \neq -2$$ and $$x \neq 2$$ .
Step 2
Divide out the common factor.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{(x+2)(x+2)}{(x+2)(x-2)}
& = \frac{\cancelred{(x+2)}(x+2)}{\cancelred{(x+2)}(x-2)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x+2}{x-2};\quad x \neq 2
\end{align*}
$$
Note that the other restriction (that $$x \neq -2$$ ) is still explicit in the final expression.
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^2 + 4x + 4}{x^2 - 4} = \frac{x+2}{x-2};\quad x \neq 2
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 3
Step 1
Factor the numerator and the denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{5x^3 -17x^2 - 12x}{x^2-4x}
& = \frac{x(5x^2 -17x - 12)}{x(x-4)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x(x - 4)(5x + 3)}{x(x-4)}
\end{align*}
$$
From the factored denominator we can see that our final answer will need to restrict $$x$$ so that $$x \neq 0$$ and $$x \neq 4$$ .
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x(x - 4)(5x + 3)}{x(x-4)}
& = \frac{\cancelred{x(x - 4)}(5x + 3)}{\cancelred{x(x-4)}}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{5x + 3}{1}\\[6pt]
& = 5x + 3; \quad x \neq 0, 4
\end{align*}
$$
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{5x^3 -17x^2 - 12x}{x^2-4x} = 5x + 3; \quad x \neq 0, 4
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 4
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{2x^2 + 26x + 84}{2x^2 + 12x - 14}
= \frac{2(x^2 + 13x + 42)}{2(x^2 + 6x - 7)}\\[6pt]
= \frac{2(x + 6)(x + 7)}{2(x + 7)(x - 1)}
\end{align*}
$$
From the factored denominator we can see that our final answer will have to restrict the $$x$$-values so that $$x \neq -7$$ and $$x \neq 1$$ .
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{2(x + 7)(x + 6)}{2(x + 7)(x - 1)}
& = \frac{\cancelred{2(x + 7)}(x + 6)}{\cancelred{2(x + 7)}(x - 1)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x + 6}{x - 1};\quad x \neq -7
\end{align*}
$$
Note that the other restriction is still explicitly part of the final expression.
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{2x^2 + 26x + 84}{2x^2 + 12x - 14} = \frac{x + 6}{x - 1};\quad x \neq -7
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 5
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{6x^3 + 57x^2 + 72x}{10x^3 + 85x^2 + 40x}
& = \frac{3x(2x^2 + 19x + 24)}{5x(2x^2 + 17x + 8)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{3x(x+8)(2x+3)}{5x(x+8)(2x+1)}
\end{align*}
$$
From the factored denominator, we can see that our final answer will need to restrict $$x$$ so that $$x \neq -8$$ , $$x \neq - \frac 1 2$$ and $$x \neq 0$$ .
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{3x(x+8)(2x+3)}{5x(2x+1)(x+8)}
& = \frac{3\cancelred{x(x+8)}(2x+3)}{5\cancelred{x(x+8)}(2x+1)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{3(2x+3)}{5(2x+1)}; \quad x \neq -8, 0
\end{align*}
$$
The other restriction (that $$x \neq - \frac 1 2$$ ) is still explicit in the final expression.
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{6x^3 + 57x^2 + 72x}{10x^3 + 85x^2 + 40x}
= \frac{3(2x+3)}{5(2x+1)}; \quad x \neq -8, 0
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 6
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{9x^2-20x-x^3}{24x -10x^2 + x^3}
& = \frac{-x(x - 5)(x - 4)}{x(x - 6)(x -4)}
\end{align*}
$$
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{-x(x - 5)(x - 4)}{x(x - 6)(x -4)}
& = \frac{-\cancelred{x}(x - 5)\cancelred{(x - 4)}}{\cancelred{x}(x - 6)\cancelred{(x - 4)}}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{-(x - 5)}{(x - 6)}\\[6pt]
& = -\frac{x - 5}{x - 6}
\end{align*}
$$
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{9x^2-20x-x^3}{24x -10x^2 + x^3}
= -\frac{x - 5}{x - 6}
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 7
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator. In this case we need to use factoring by grouping.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^3 + 4x^2 + 4x + 16}{x^3+4x^2 - 3x - 12}
& = \frac{(x^3 + 4x^2) + (4x + 16)}{(x^3+4x^2) + (- 3x - 12)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x^2(x + 4) + 4(x + 4)}{x^2(x+4) + -3(x + 4)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{(x + 4)(x^2 + 4)}{(x + 4)(x^2 - 3)}
\end{align*}
$$
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{(x + 4)(x^2 + 4)}{(x + 4)(x^2 - 3)}
& = \frac{\cancelred{(x + 4)}(x^2 + 4)}{\cancelred{(x + 4)}(x^2 - 3)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x^2 + 4}{x^2 - 3}
\end{align*}
$$
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^3 + 4x^2 + 4x + 16}{x^3+4x^2 - 3x - 12} = \frac{x^2 + 4}{x^2 - 3}
\end{align*}
$$
Problem 8
Step 1
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Step 1 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^3 + 27}{x^2 + 12x + 27}
= \frac{(x + 3)(x^2 - 3x +9)}{(x + 3)(x + 9)}
\end{align*}
$$
Step 2
Divide out the common factors.
Step 2 Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{(x + 3)(x^2 - 3x +9)}{(x + 3)(x + 9)}
& = \frac{\cancelred{(x + 3)}(x^2 - 3x +9)}{\cancelred{(x + 3)}(x + 9)}\\[6pt]
& = \frac{x^2 - 3x +9}{x + 9}
\end{align*}
$$
Answer
Show Answer
$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{x^3 + 27}{x^2 + 12x + 27} = \frac{x^2 - 3x +9}{x + 9}
\end{align*}
$$
Error : Please Click on "Not a robot", then try downloading again.